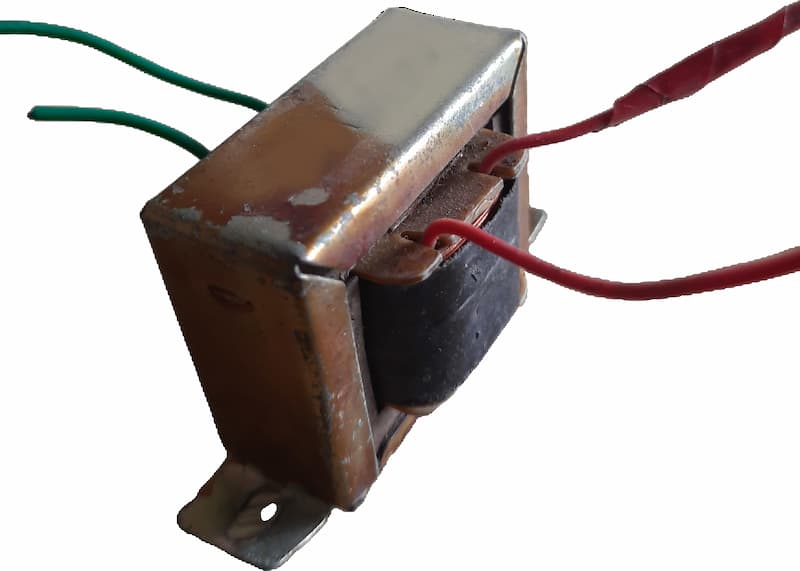
Why is varnish sometimes applied to transformer windings?
What is varnish? Varnish is a protective coating/paint that is often used in the furniture industry to give a finishing and protect wood.
Read More
Published on Jul 15, 2023 by Skipper
Electrical insulators are materials that resist the flow of electric current. They are used to prevent electric shocks, short circuits, and overheating in electrical equipment, such as motors, transformers, cables, etc. Electrical insulators have different temperature ratings, which indicate how much heat they can withstand without losing their insulating properties. These ratings are based on the types of materials used and their thermal stability.
The temperature ratings of electrical insulators are divided into seven classes: Y, A, E, B, F, H, and C. Each class has a maximum temperature limit in degrees Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), and Kelvin (K). The table below shows the temperature limits for each class of insulation.
| Insulation Class | Maximum temperature (° C, Celsius) | Maximum temperature (° F, Fahrenheit) | Maximum temperature (K, Kelvin) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y | 90 | 194 | 363.15 |
| A | 105 | 221 | 378.15 |
| E | 120 | 248 | 393.15 |
| B | 130 | 266 | 403.15 |
| F | 155 | 311 | 428.15 |
| H | 180 | 356 | 453.15 |
| C | 180+ | 356+ | 453.15+ |
The classes of insulation are also associated with different types of materials, which have different physical and chemical properties. Some examples of materials used for each class of insulation are:
Class Y (90 °C): Silk, cotton, certain thermoplastics that soften above 90 °C.
Class A (105 °C): Reinforced silk, cotton and paper (with impregnated varnish or insulation oil).
Class E (120 °C): Powder plastics, polyurethane, molded polyvinyl epoxy resins, polyethylene terephthalate.
Class B (130 °C): Inorganic materials such as asbestos, glass fibers, mica with varnish.
Class F (155 °C): Mica, class B materials that perform well at higher temperatures.
Class H (180 °C): Fiberglass, mica, asbestos impregnated in silicone rubber.
Class C (180 °C+): Polyimide films, quartz, mica, teflon, polyimide enamel.
Insulating materials are may be in the form of solid, liquid and gas.
Solid - Mica, teflon, cotton tape, PVC tape, etc.
Liquid - Insulating Oil.
Gases - SF6 Gas, inert gases, etc.
It is important to choose the right class of insulation for the intended application and environment of the electrical equipment. Using a lower class of insulation than required can result in damage or failure of the equipment due to excessive heat. Using a higher class of insulation than required can result in unnecessary cost and weight of the equipment. Therefore, it is advisable to understand the temperature requirement of your system as well as selecting the best suitable class available for you from the manufacturer’s specifications and recommendations.
In this article, we have covered:

What is varnish? Varnish is a protective coating/paint that is often used in the furniture industry to give a finishing and protect wood.
Read More